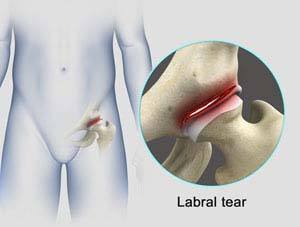
Hip Labral Tear
Anatomy of the Hip Joint
The hip joint is a ball and socket joint in which the head of the femur is the ball and the acetabulum forms the socket. The labrum helps to deepen the socket and provide stability to the joint. It also acts as a cushion and enables smooth movement of the joint.
What is a Hip Labral Tear?
A hip labral tear is an injury to the labrum, the cartilage that surrounds the outside rim of your hip joint socket.
Causes of Hip Labral Tears
A tear in the labrum of the hip can result from:
- Traumatic injury, such as a motor vehicle accident
- Participating in sports such as football, soccer, basketball and snow skiing
- Repetitive movements
- Weight-bearing activities over time, which can lead to joint wear and tear
- Degenerative changes to the hip joint in the elderly
Symptoms of Hip Labral Tears
You may not have symptoms. However, sometimes, you may experience:
- Pain in the hip or groin area
- Catching or locking sensation in the hip joint
- Significant restriction in hip movement
Diagnosis of a Hip Labral Tear
Your doctor will order certain tests to determine the cause of your hip pain.
X-rays of the hip allow your physician to rule out other possible conditions such as fractures or structural abnormalities.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be ordered to evaluate the labrum. An injection of contrast material into the hip joint space at the time of the MRI can help detect the labral tears much more clearly.
The injection of a local anesthetic into the joint space is sometimes performed to confirm the location of the pain. If the injection completely relieves your pain, it is likely that the cause of the problem is located inside the hip joint.
Treatment Options for a Hip Labral Tear
The treatment for a hip labral tear will depend on the severity of the condition. If you have a minor labral tear, you will recover within a few weeks with the help of non-surgical treatments, which include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications can be helpful in relieving pain and reducing inflammation associated with labral tears. Your doctor may also recommend cortisone injections to alleviate the pain associated with a hip labral tear.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy that helps to improve hip range of motion, strength, and stability are also recommended.
However, severe cases may require arthroscopic surgery to remove or repair the torn portion of the labrum.
Surgery for Hip Labral Tears
Hip arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole surgery or minimally invasive surgery, is a surgical procedure in which an arthroscope, a narrow tube with a tiny camera on the end, is used to assess and repair damage to the hip.
The surgery is performed under general, spinal or local anesthesia.
Your surgeon will make 2 or 3 small incisions around the hip joint area. The arthroscope is inserted into the hip joint through one of the incisions to view the labral tear. The camera attached to the arthroscope displays the image of the joint on the monitor. A sterile solution will be pumped into the joint to provide a clear view and room to work. Through the other incisions, specially designed instruments are inserted. Your surgeon repairs the torn tissue by sewing it back together or removes the torn piece altogether, depending upon the cause and extent of the tear. After the completion of the procedure, the arthroscope and instruments are removed and the incisions are closed.
Postoperative Care following Surgery for Hip Labral Tears
Following the surgery, you will be given instructions on caring for your incisions, activities to avoid and exercises to perform for a fast recovery and a successful outcome. Physical therapy will be recommended by your doctor to restore your strength and mobility. Your doctor will also prescribe pain medications to keep you comfortable.
Risks and Complications of Surgery for Hip Labral Tears
The possible risks and complications specific to arthroscopic hip surgery include:
- Infection
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Blood vessel or nerve damage
- Hemarthrosis (bleeding inside the joint)
- Failure to relieve pain
Related Topics:
- Hip Adductor Injuries
- Pediatric Femur Fracture
- Stress Fractures of the Hip
- Avulsion Fractures of the Pelvis
- Hip Injury
- Stem Cell Therapy for Hip Injuries
- Gluteus Tendon Tear
- Hip Pain
- Snapping Hip Syndrome
- Hip Bursitis
- Femoroacetabular Impingement
- Avascular Necrosis
- Hip Fracture
- Hip Dislocation
- Hip Labral Tear
- Hip Instability
- Hip Groin Disorders
- Subtrochanteric Hip Fracture
- Hip Abductor Tears
- Hip Synovitis
- Developmental Dysplasia
- Legg-Calve-Perthes-Disease
- Irritable Hip
- Hip Tendonitis
- Hip Pointer
- Transient Osteoporosis of the Hip
- Osteoarthritis of the Hip
- Inflammatory Arthritis of the Hip
- Groin Injuries in Athletes
- Periprosthetic Hip Infection
- Hamstring Injuries